Understanding why the plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane starts with a deep dive into its structure and function. This membrane, enveloping every cell, is pivotal for life, acting as a gatekeeper that controls the flow of substances in and out. It’s composed of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins that help it to selectively allow passage to certain molecules while barring others, a mechanism critical to the cell’s survival and health.
Understanding Selective Permeability
The concept of selective permeability is central to discussing why the plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane. This selective access provided by the plasma membrane ensures that essential nutrients and ions can enter the cell while metabolic wastes and toxic substances are expelled. Such selectivity is crucial for maintaining the chemical milieu necessary for the cell’s optimal function.
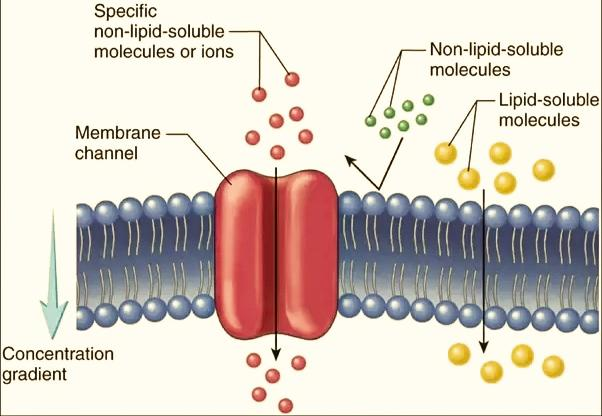
Mechanisms Behind the Selectivity of the Plasma Membrane
Exploring why the plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane involves examining the specific transport mechanisms it employs:
- Passive Transport: This mode allows substances to move across the plasma membrane without the cell expending energy, crucial for maintaining energy efficiency.
- Active Transport: This requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient, essential for accumulating nutrients and expelling toxins against their natural flow.
These mechanisms highlight the plasma membrane’s dynamic ability to adjust cellular conditions precisely and responsively, underscoring why the plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Also Read:
- Crickex: is it reliable? Full analysis for 2024
- History of Poker Cards
- Why Is Respiration Considered An Exothermic Reaction Explain
Factors Influencing the Permeability of the Plasma Membrane
Several factors influence why the plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane, including environmental conditions like temperature and pH, which can alter its fluidity and functioning. The size and solubility of molecules also play critical roles, as the plasma membrane selectively filters substances based on these characteristics.
Biological Significance of Selective Permeability
The reason why the plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane is fundamentally linked to its biological importance. This selective permeability is essential for cellular signaling, nutrient absorption, and waste removal, facilitating complex biological processes and maintaining homeostasis within the body.
Case Studies and Research on Plasma Membrane Permeability
In-depth research and case studies provide insights into why the plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane. Studies in varied environmental conditions reveal how cells modify their membrane properties to survive, offering valuable lessons for biomedical and environmental applications.
Practical Applications of Understanding the Plasma Membrane
The study of why the plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane has profound implications in medical and biotechnological fields. It aids in the development of targeted therapies and biotechnological innovations that mimic or alter membrane properties for improved health outcomes.
FAQs on Why the Plasma Membrane Is Selectively Permeable
The plasma membrane selectively allows certain substances to pass through while blocking others, crucial for maintaining cellular environment and function.
Transport proteins facilitate the movement of specific substances across the membrane, ensuring essential ions and molecules can enter or exit the cell as needed.
Environmental factors like temperature and pH can alter the membrane’s fluidity and structure, affecting its function and the transport of substances.
Yes, artificial membranes mimicking biological selectivity are used in pharmaceuticals, water purification, and biotechnology for targeted applications.
Compromised membrane permeability can lead to cell damage or death from disrupted nutrient and waste exchange, potentially resulting in various diseases.
Knowledge of membrane permeability aids in designing effective drug delivery systems and treatments that modulate cellular functions, crucial for targeting diseases like cancer.
